Neurally adjusted ventilation assist for critically ill patients
Neurally adjusted ventilatory assist (NAVA) delivers airway pressure (P_aw) in proportion to the electrical activity of the diaphragm (EAdi) using an adjustable proportionality constant (NAVA level, cm H_20/microvolt). During systematic increases in the NAVA level, feedback-controlled down-regulation of the EAdi results in a characteristic two-phased response in P_aw and tidal volume (Vt). The transition from the 1st to the 2nd response phase allows identification of adequate unloading of the respiratory muscles with NAVA (NAVA_AL). We aimed to develop and validate a mathematical algorithm to identify NAVA_AL. More details can be found in published journal manuscript 7 [pdf].
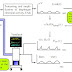
Signals like airway pressure and electrical activity of the diaphragm are recorded.
Software developed in Matlab for the automatic estimation of NAVA adequate level.
The methodology presented graphically.